Epithelial Cells in Urine: Normal Range, Causes, and When to See a Doctor
2 min read
By DocGenie , Published on - 06 December 2025What Are Epithelial Cells in Urine?
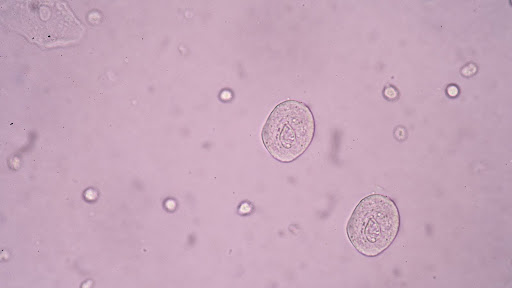
Epithelial cells are tiny cells that form the protective lining of your urinary tract — including your kidneys, bladder, and urethra. These cells naturally shed and can be found in small numbers in your urine. Think of it like a few bricks falling from a well-built wall during routine maintenance — it’s normal. But if too many cells are present, or certain types, it can be a warning sign of irritation, infection, or other health issues.
What Are Epithelial Cells?
Epithelial cells serve as the body's shield — they protect the tissues and help filter waste products. These cells are constantly renewing themselves, which naturally produces some cell shedding into urine. The presence of these cells can indicate how healthy or irritated your urinary system is.
Normal Range of Epithelial Cells in Urine
Laboratories typically consider less than 15 epithelial cells per high power field (HPF) on microscopic examination as normal. Numbers beyond that suggest there might be irritation or damage somewhere along your urinary tract that requires investigation.
Common Causes of Increased Epithelial Cells
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): The most common culprit. Infections cause inflammation and increased shedding of lining cells.
- Kidney Diseases: Conditions such as glomerulonephritis provoke inflammation, raising epithelial cell counts.
- Inflammation or Injury: Kidney stones, catheter use, or trauma to the urinary tract increase cell shedding.
- Sample Contamination: Poor hygiene during sample collection can introduce false positives.
- Other Health Issues: Tumors, autoimmune diseases, or chronic irritation can also elevate levels.
How to Reduce Epithelial Cells in Urine
- Prompt treatment of infections with antibiotics.
- Drinking plenty of water to flush out bacteria.
- Practicing proper hygiene to prevent contamination.
- Avoiding unnecessary catheterization or irritants.
- Managing chronic kidney or autoimmune issues effectively.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult your healthcare provider if you experience symptoms such as:
- Burning or pain on urination
- Frequent urges to urinate
- Blood in urine
- Fever or flank pain
- Persistent high epithelial cell counts in tests without clear reason
The Importance of Monitoring Urinary Health
Regular urine analysis helps catch problems early. Services like DocGenie facilitate easy access to medical advice and intervention for urinary symptoms or concerns.