What is Atopic Dermatitis? Signs, Symptoms, and Natural Remedies
5 min read
By DocGenie , Published on - 13 November 2024Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness. It affects people of all ages, but it is especially common in children. Understanding what is eczema, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help manage this condition effectively. In this guide, we explore what is atopic dermatitis, what is the reason for eczema, various types of eczema, and natural remedies for relief.
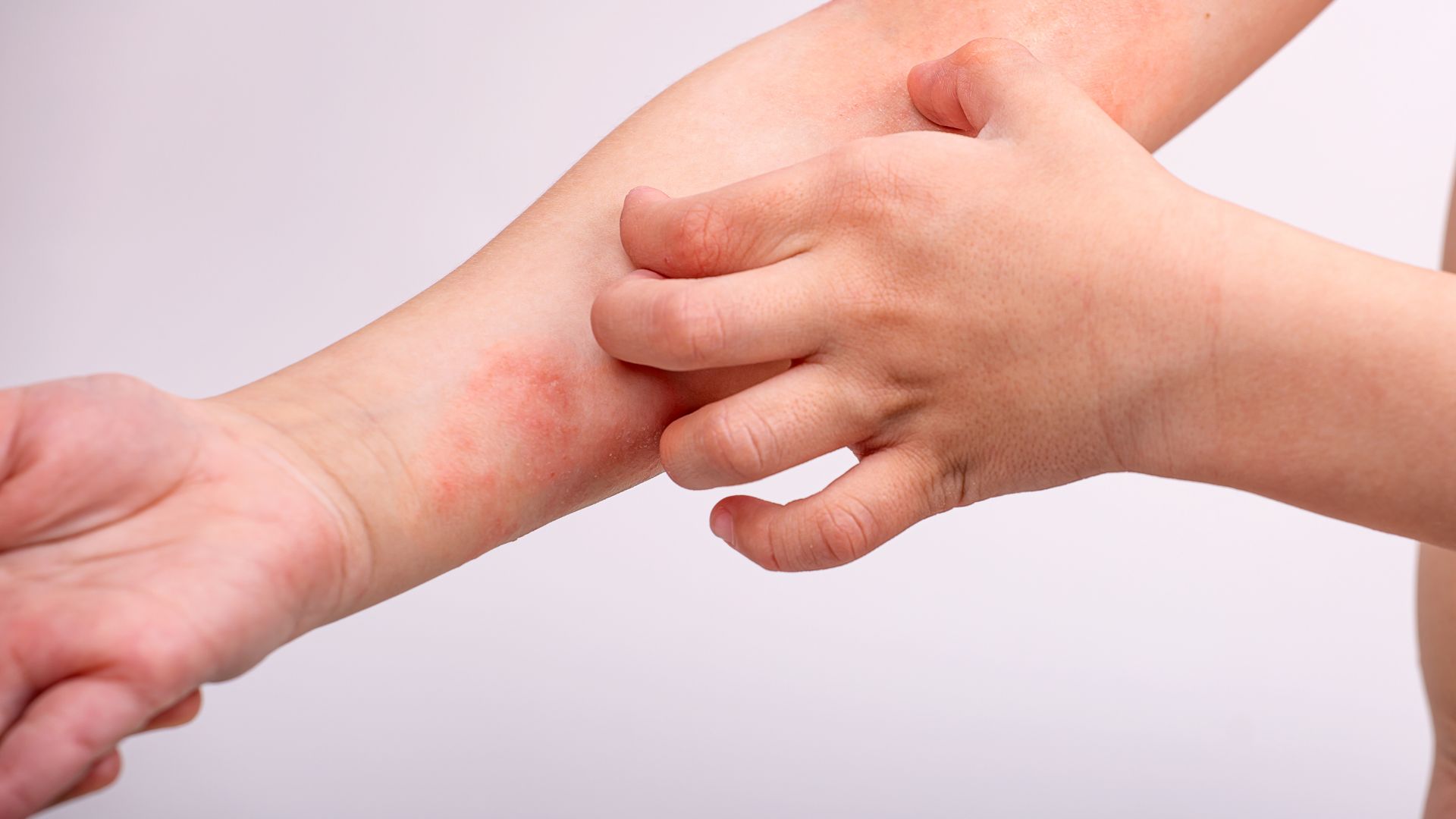
What is Eczema?
Eczema is an umbrella term for skin conditions that cause inflammation, irritation, and intense itching. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema and is often associated with allergies, asthma, and hay fever.
What is the Reason for Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:- Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies increases the risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An overactive immune response triggers inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Irritants such as smoke, pollution, dust, and harsh chemicals can worsen symptoms.
- Allergens: Certain foods (dairy, nuts, eggs), pollen, pet dander, and mold can trigger eczema.
- Weather Conditions: Cold, dry air or excessive heat can cause flare-ups.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: People with eczema have a weaker skin barrier, leading to moisture loss and increased sensitivity to irritants.
Signs and Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema symptoms vary in severity but often include:- Itchy, inflamed skin
- Red or brownish patches on the face, neck, elbows, knees, or hands
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Oozing or crusting blisters (in severe cases)
- Thickened, rough skin from excessive scratching
Types of Eczema
Eczema is classified into different types based on its triggers and symptoms. The most common types include:- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, linked to genetics and immune system dysfunction.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by direct contact with irritants (soaps, detergents, cosmetics, metals, etc.).
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Appears as round, coin-shaped spots on the skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas of the skin, such as the scalp (dandruff) and face.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Occurs in people with poor circulation, especially in the lower legs.
- Neurodermatitis: A chronic form caused by repetitive scratching or rubbing.
| Type | Causes/Triggers | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Genetics, immune dysfunction | Itchy, inflamed skin; often linked to allergies |
| Contact Dermatitis | Irritants (soaps, detergents, metals) | Red, itchy rash at the point of contact |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Unknown; possibly stress, allergies | Small, itchy blisters on hands and feet |
| Nummular Eczema | Unknown; possibly insect bites, skin injury | Coin-shaped spots on the skin |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Yeast overgrowth, oily skin | Dandruff, scaly patches on the scalp and face |
| Stasis Dermatitis | Poor circulation | Occurs on lower legs; swelling, redness, itching |
| Neurodermatitis | Repetitive scratching/rubbing | Thickened, leathery skin in affected areas |
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options
While there is no cure for eczema, several treatments help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups:- Medical Treatments
- Topical Steroids: Reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moisturizers: Keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
- Antihistamines: Help control itching, especially at night.
- Immunosuppressants: Used for severe cases when other treatments fail.
- Biologic Therapies: Newer treatments that target the immune response causing eczema.
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, and synthetic fabrics.
- Use a humidifier to prevent dry air from worsening symptoms.
- Wear loose, breathable clothing made of cotton.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
Atopic Dermatitis Remedy: Natural Treatments for Eczema Relief
Many people prefer natural remedies for eczema to avoid potential side effects of medications. Here are some effective options:- Coconut Oil
- Has antimicrobial properties and provides deep hydration.
- Apply virgin coconut oil to affected areas twice daily.
- Aloe Vera
- Soothes inflammation and relieves itching.
- Use fresh aloe vera gel or a natural aloe-based cream.
- Oatmeal Baths
- Colloidal oatmeal reduces redness, itching, and irritation.
- Add a cup of finely ground oats to warm bathwater and soak for 15–20 minutes.
- Honey
- Natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent.
- Apply raw honey to affected skin for 20 minutes before rinsing.
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Helps restore the skin’s pH balance.
- Mix one part vinegar with one part water and apply using a cotton ball.
- Probiotics and Omega-3s
- Improve gut health and reduce inflammation.
- Consume yogurt, kefir, flaxseeds, and fatty fish.
- Essential Oils
- Tea tree oil and chamomile oil can help soothe eczema-prone skin.
- Always dilute essential oils with a carrier oil before applying.
Preventing Eczema Flare-Ups
- Keep skin moisturized at all times.
- Use fragrance-free skincare products.
- Take short, lukewarm showers instead of hot baths.
- Identify and avoid trigger foods (dairy, gluten, nuts, etc.).
- Manage stress through meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises.
When to See a Doctor?
If your eczema symptoms are severe, do not improve with home remedies, or lead to infection (pus, swelling, or fever), consult a dermatologist for advanced treatment options.Final Thoughts
Eczema, particularly atopic dermatitis, can be challenging, but with the right atopic dermatitis treatment and atopic dermatitis remedy, it is manageable. By following a healthy skincare routine, using natural treatments, and avoiding triggers, you can control symptoms and improve your quality of life.
For expert medical advice and dermatology consultations, consider DocGenie’s telemedicine platform to receive personalized guidance for eczema management.
Author Details

Dr.Rachna Kucheria
MD (Community Medicine) AIIMS New Delhi
MD (Family Medicine) USC California
Obesity Medicine Certification The American Board of Obesity Medicine
30+ Years of experience